Tax Multiplier Formula: How This Dirty Little Secret Boosts GDP by 20% (And Why You Should Care)

Opening Paragraph
Did you know that a simple economic concept called the tax multiplier formula can potentially boost a country’s GDP by up to 20%? This “dirty little secret” of economists and policymakers has far-reaching implications for economic growth, employment, and even your personal finances. Whether you’re an investor, a business owner, or just someone curious about how economies work, understanding the tax multiplier is crucial. In this post, we’ll break down what the tax multiplier formula is, how it impacts GDP, and why it matters to you. (tax multiplier formula, GDP growth, economic policy)
What is the Tax Multiplier Formula?
The tax multiplier formula is an economic tool used to measure the impact of changes in taxation on a country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Simply put, it calculates how much GDP changes in response to a change in taxes. The formula is derived from the broader concept of the fiscal multiplier, which assesses the effects of government spending and taxation on economic activity.
Key Components of the Tax Multiplier:
- Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC): The fraction of additional income that households spend rather than save.
- Change in Taxes: The amount by which taxes are increased or decreased.
The formula is:
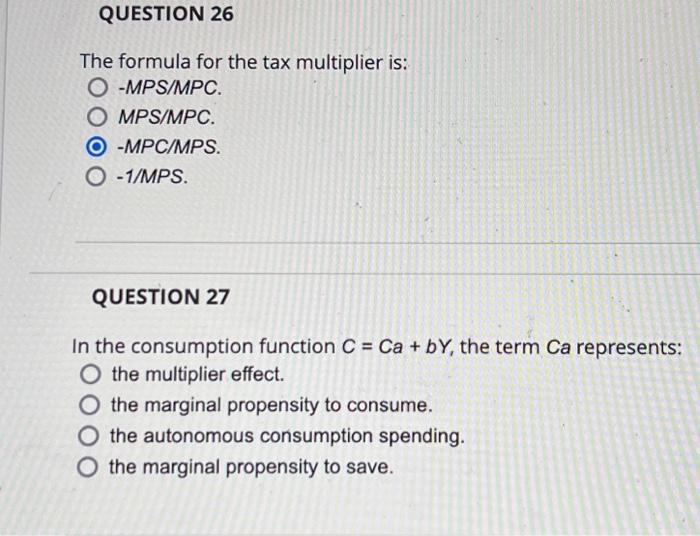
Tax Multiplier = -MPC / (1 - MPC)
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| MPC | Marginal Propensity to Consume |
| Tax Multiplier | Measures the effect of tax changes on GDP |

💡 Note: A negative tax multiplier indicates that an increase in taxes reduces GDP, while a decrease in taxes boosts it.
How Does the Tax Multiplier Boost GDP by 20%?
The tax multiplier’s power lies in its ability to amplify economic changes. When taxes are cut, households and businesses have more disposable income, which they spend or invest. This increased spending creates a ripple effect, stimulating economic activity across sectors.
Example Scenario:
If the government reduces taxes by 1 billion and the MPC is 0.8, the tax multiplier would be -0.8 / (1 - 0.8) = -4. This means GDP could increase by 4 billion for every $1 billion tax cut. Over time, this effect can accumulate, potentially boosting GDP by 20% or more, depending on the scale and timing of tax changes.
Why Should You Care About the Tax Multiplier?
Understanding the tax multiplier isn’t just for economists—it has real-world implications for everyone:
- Investors: Tax policies can influence market trends and stock performance.
- Business Owners: Changes in taxes affect consumer spending and business profitability.
- Individuals: Tax cuts can mean more money in your pocket, while increases may reduce disposable income.
💡 Note: Stay informed about fiscal policies to make better financial decisions.
Checklist: How to Leverage the Tax Multiplier

- Monitor Tax Policies: Keep an eye on government announcements about tax changes.
- Analyze MPC Trends: Understand consumer spending behavior in your region.
- Plan Your Finances: Adjust your budget based on expected tax changes.
- Invest Wisely: Consider sectors likely to benefit from increased economic activity.
Final Thoughts
The tax multiplier formula may seem like a complex economic concept, but its impact on GDP and personal finances is undeniable. By understanding how it works, you can make more informed decisions and navigate economic changes with confidence. Whether you’re an investor, business owner, or individual, this “dirty little secret” is one you’ll want to keep in mind. (tax multiplier formula, GDP growth, economic policy)
What is the tax multiplier formula?
+
The tax multiplier formula measures the impact of tax changes on GDP. It is calculated as -MPC / (1 - MPC), where MPC is the Marginal Propensity to Consume.
How does a tax cut boost GDP?
+
A tax cut increases disposable income, leading to higher consumer spending and investment. This stimulates economic activity, amplifying GDP growth through the tax multiplier effect.
Why is the tax multiplier negative?
+
The tax multiplier is negative because an increase in taxes reduces disposable income, leading to a decrease in GDP. Conversely, a tax cut has a positive effect on GDP.
